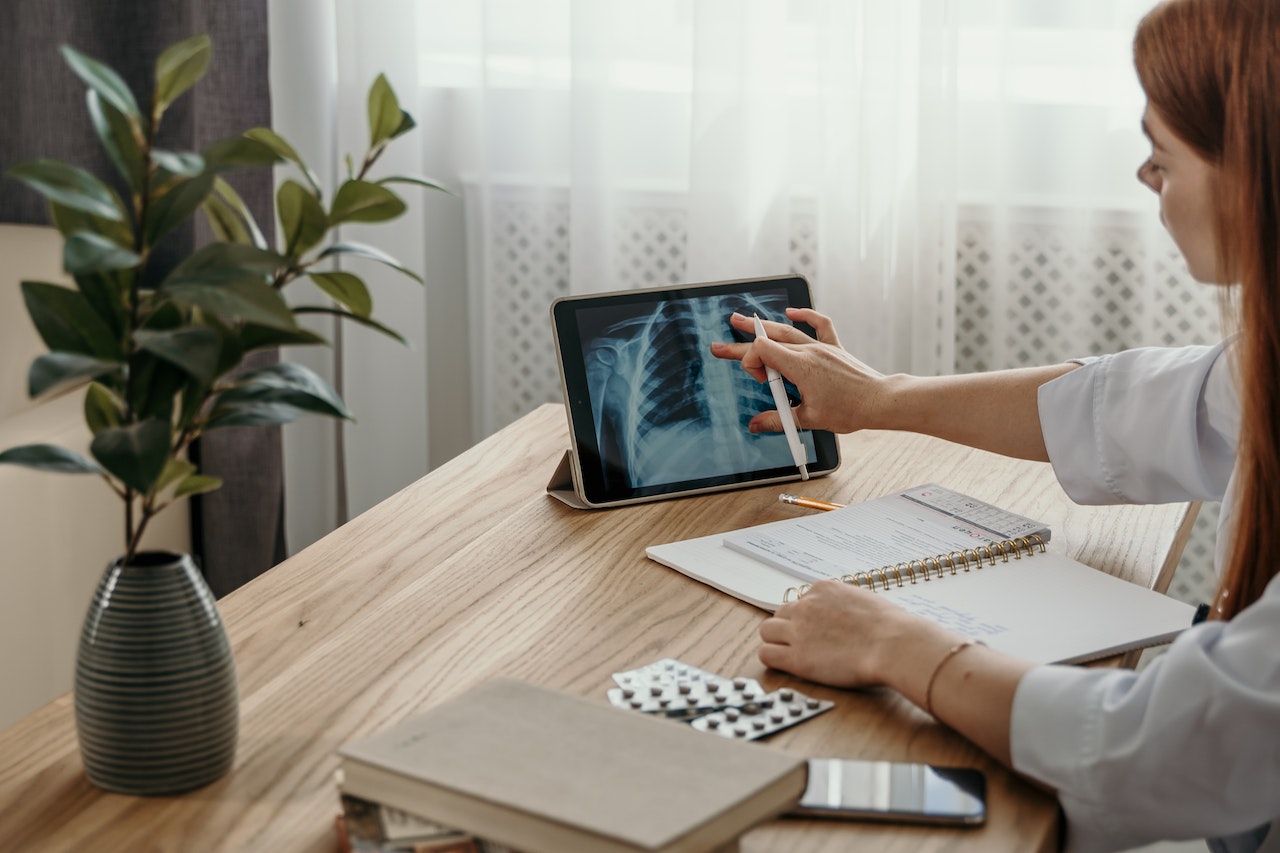
In the realm of modern cardiology, virtual FFR is emerging as a revolutionary technique for assessing coronary artery health. This innovative approach leverages advanced computational models and imaging technologies to provide accurate and non-invasive assessments of blood flow within the coronary vessels. Virtual FFR involves creating a computational model of the patient’s coronary arteries based on medical imaging data, such as CT scans. This model simulates blood flow and pressure within the vessels, allowing clinicians to calculate FFR values without the need for invasive procedures. The result is a detailed assessment of the functional significance of coronary lesions.
The power of computational fluid dynamics how it works
At the heart of virtual FFR lies computational fluid dynamics (CFD), a branch of engineering that simulates fluid flow patterns. CFD algorithms are applied to the patient’s coronary anatomy, factoring in vessel dimensions, blood flow rates, and other variables. This simulation provides insights into pressure gradients and potential obstructions, aiding in the determination of lesion severity. The adoption of virtual FFR brings numerous benefits to clinical practice. Firstly, it eliminates the need for invasive procedures like traditional FFR, which involves threading a wire into the coronary artery. This minimizes patient discomfort and procedural risks. Secondly, the technique provides rapid results, enabling timely decision-making for treatment strategies.
Empowering treatment decisions a patient centric approach
By combining anatomical imaging with functional information, virtual FFR empowers cardiologists to make well-informed treatment decisions. The technique assists in identifying lesions that require intervention, while also determining optimal treatment methods such as stenting or bypass surgery. This personalized approach enhances patient outcomes and quality of life. As technology continues to advance, the accuracy and clinical utility of virtual FFR are expected to increase. Improvements in imaging resolution and computational algorithms will further refine the technique’s capabilities. The integration of virtual FFR into routine practice could potentially transform how coronary artery disease is diagnosed and managed.